Python -- Lists and Tuples
List and Tuple are
built-in container types defined in Python. Objects of both these types can
store different other objects that are accessible by index. List as well as
tuple is a sequence data type, just as string. List as well as tuple can store
objects which need not be of same type.
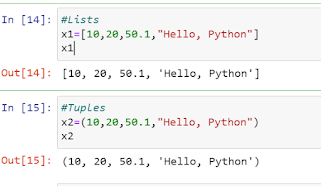
List : A List is an ordered collection of items
(which may be of same or different types) separated by comma and enclosed in
square brackets.
Tuple: Tuple looks similar to list. The only
difference is that comma separated items of same or different type are enclosed
in parentheses.
Differences between List & Tuple:
The obvious difference is the use of square brackets []
in List and parentheses () in tuple as enclosures. However, the important
difference is that List as a mutable object and Tuple is an immutable object.
If
contents of an object can be modified in place, after it has been instantiated,
is a mutable object. On the other hand, any operation on immutable object that
tries to modify its contents is prohibited.
Various methods to perform operations on list are below::
|
Append() |
Appends an
object to the end of the list |
|
Copy() |
Makes a copy of
list |
|
Count() |
Returns number
of occurrences of value in list |
|
Extend() |
Extends the list
by appending elements from another list/tuple |
|
Insert() |
Insert objects
in the list based on index |
|
Pop() |
Removes and
returns last item at given index .Raises IndexError if list is empty or index
is out of range. |
|
Remove() |
Removes first
occurrence of value in the list. Raises ValueError if the value is not
present. |
|
Clear() |
Removes all items
from the list |
Comments
Post a Comment